System Program and its type : Operating System
 System programming may be defined as the act of creating System Software by using the System Programming Languages. A system program offers an environment in which programs may be developed and run. In simple terms, the system programs serve as a link between the user interface (UI) and system calls. Some system programs are only user interfaces, and others are complex. For instance, a compiler is complicated system software.
System programming may be defined as the act of creating System Software by using the System Programming Languages. A system program offers an environment in which programs may be developed and run. In simple terms, the system programs serve as a link between the user interface (UI) and system calls. Some system programs are only user interfaces, and others are complex. For instance, a compiler is complicated system software.
The system program is a component of the OS, and it typically lies between the user interface (UI) and system calls. The system user view is defined by the system programs, not the system call, because the user view interacts with system programs and is closer to the user interface.
Types of the System Program
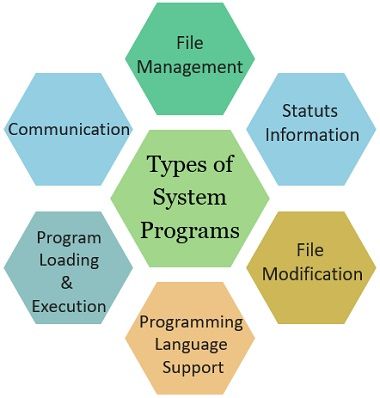
There are mainly six types of system programs. These are classified as follows:
- File Management
- Status Information
- File Modification
- Programming-Language support
- Program Loading and Execution
- Communication
File Management : It is a collection of specific information saved in a computer system's memory. File management is described as manipulating files in a computer system, including the creation, modification, and deletion of files.
Status Information : Status information is information about the input, output process, storage, and CPU utilization time, how the process will be computed in how much memory is necessary to execute a task.
File Modification : These system programs are utilized to change files on hard drives or other storage media. Besides modification, these programs are also utilized to search for content within a file or to change content within a file.
Programming-Language Support : The OS includes certain standard system programs that allow programming languages such as C, Visual Basic, C++, Java, and Pearl. There are various system programs, including compilers, debuggers, assemblers, interpreters, etc.
Program Loading and Execution : After Assembling and Compiling, the program must be loaded into the memory for execution. A loader is a component of an operating system responsible for loading programs and libraries, and it is one of the most important steps to starting a program. The system includes linkage editors, relocatable loaders, Overlay loaders, and loaders.
Communication : System program offers virtual links between processes, people, and computer systems. Users may browse websites, log in remotely, communicate messages to other users via their screens, send emails, and transfer files from one user to another.