Basic Functions of OS
Basic functions of operating systems are :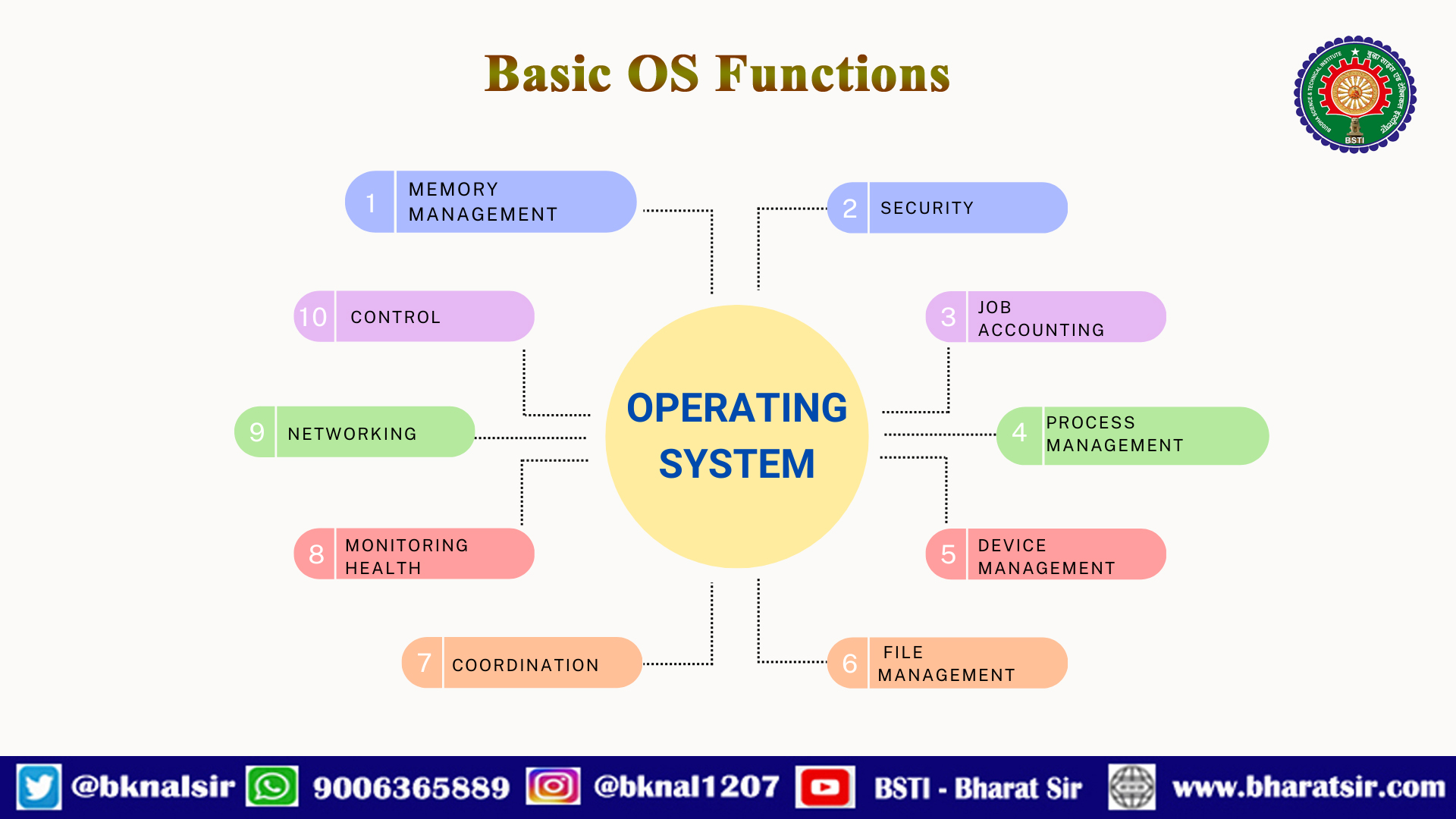
- Memory Management
- Security
- Job Accounting
- Process Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Coordination
- Monitoring Health
- Networking
- Control
Memory Management : An operating system manages the allocation and deallocation of the memory to various processes and ensures that the other process does not consume the memory allocated to one process.
Security : The operating system provides various techniques which assure the integrity and confidentiality of user data. Following security measures are used to protect user data:
- Protection against unauthorized access through login.
- Protection against intrusion by keeping Firefall active.
- Protecting the system memory against malicious access.
- Displaying messages related to system vulnerabilities.
Job Accounting : In a multitasking OS where multiple programs run simultaneously, the operating system determines which applications should run in which order and how time should be allocated to each application.
Processor Management : An operating system manages the processor’s work by allocating various jobs to it and ensuring that each process receives enough time from the processor to function properly.
Device Management : There are various input and output devices. An OS controls the working of these input-output devices. It receives the requests from these devices, performs a specific task, and communicates back to the requesting process.
File Management : An operating system keeps track of information regarding the creation, deletion, transfer, copy, and storage of files in an organized way. It also maintains the integrity of the data stored in these files, including the file directory structure, by protecting against unauthorized access.
Coordination between other software and users : Between the user and the system hardware, the operating system acts as a bridge. As needed by the user, it organises and allocates tasks to various components of the software, such as interpreters, compilers, etc.
Monitoring Health Control Over System Performance : overall system health to help improve performance. records the response time between service requests and system response to having a complete view of the system’s health. This can help improve performance by providing important information needed to troubleshoot problems.
Networking : Networking highly depends on operating systems. Distributed systems are a typical example, where a server OS can guarantee consistency among the distributed PCs.
The operating system in such a system enables the connection of several independent and geographically dispersed computers via a single communication channel.
Control / Controlling system performance : Controlling system performance is critical to managing computer systems and ensuring their efficient operation. It involves various techniques and tools to monitor, optimize, and maintain the performance of hardware, software, and networks to meet user expectations and requirements. Controlling system performance helps avoid bottlenecks, reduce response times, and maximize resource utilization.